Part 3 – Preparing the Windows 10 Golden Image and publishing the pool
What exactly is a golden image and why is it so important? Golden image is the base image of the operating system with all the necessary applications, settings and configurations. It is used as a source for mass creation of virtual desktops for end users. Proper preparation of golden image saves time, optimizes the use of resources and provides users with uniform, efficient working environments.
The first step is to prepare the machine on vCenter, to do this, log into vCenter and right-click on the cluster level and select New Virtual Machine
In the wizard window, select the first option Create a new virtual machine
Then enter the name of the machine
In the next step, decide whether the machine should be placed in a specific resource pool or whether the machine should use all the cluster’s resources. In this configuration, the entire cluster has been selected.
Next, choose the storage on which the machine will be stored, in the case of the configuration in Monetrax it will be vSAN, of course it is also possible to use an array
The next screen depending on the version of vCenter allows you to choose the version of the configuration, you can leave this option default
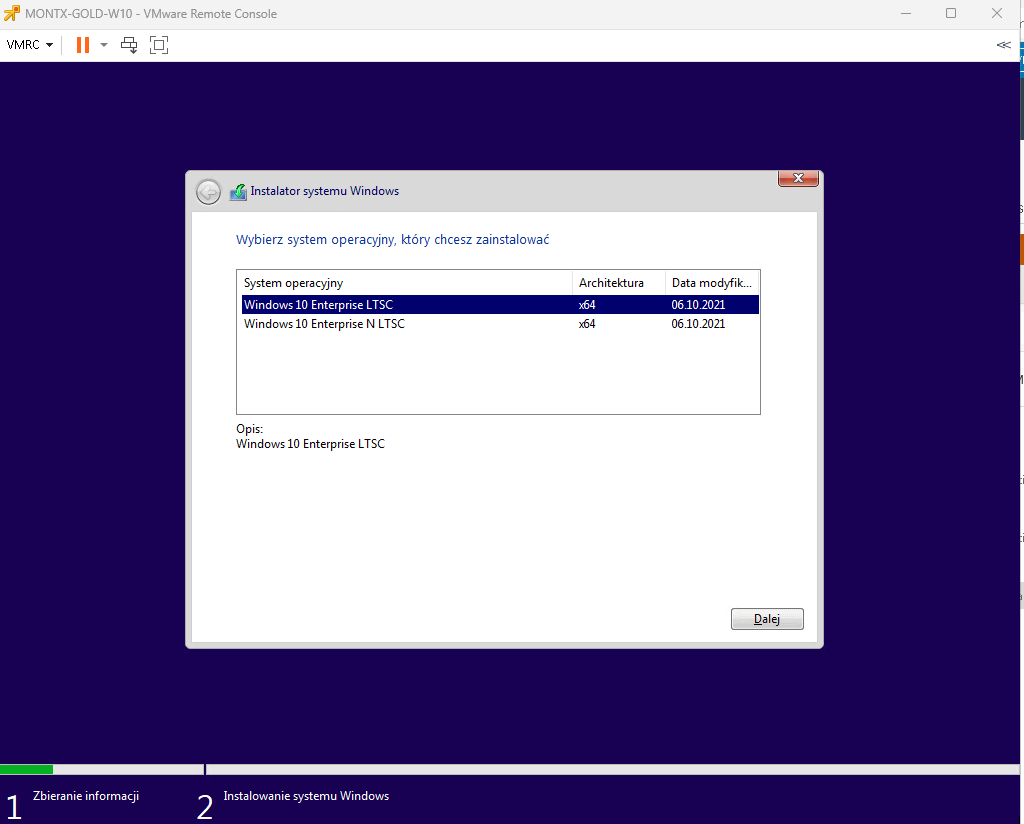
The next screen allows you to choose the operating system will be installed, in this case Windows 10
The machine parameters configuration screen allows you to configure, for example, vCPU, RAM, disk size. In the case of golden image, the following parameters will be set:
| Parameter | Value |
| vCPU | 2 |
| RAM | 8 GB |
| Disk size | 50 GB |
| Port group | DPG-MONTX-VDI |
| Network card type | VMNETX3 |
| Video card | 128 MB |
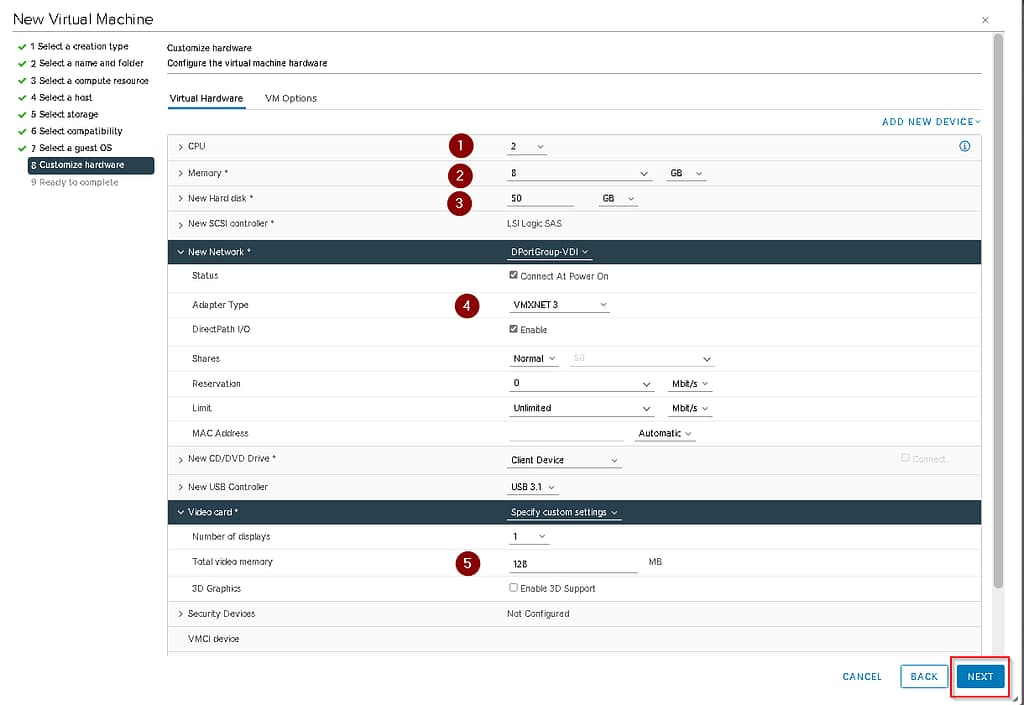
The last screen shows a summary of the machine configuration.
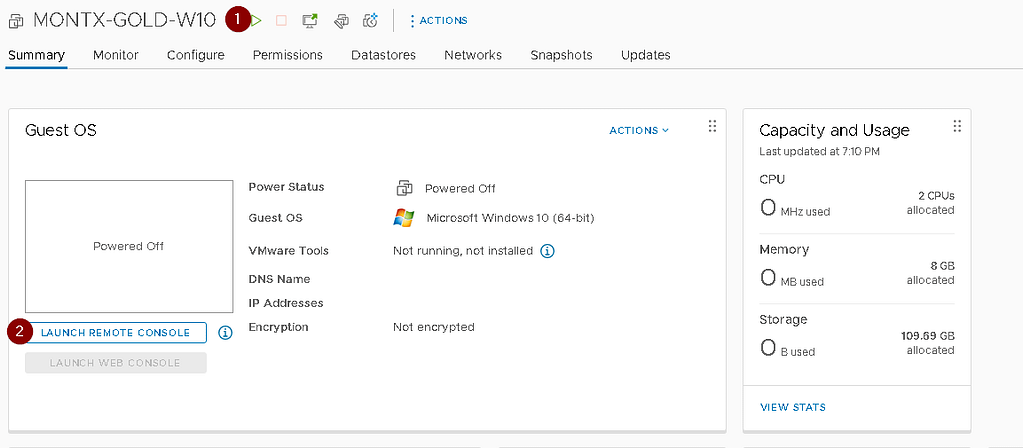
Once the machine has been created, navigate to it, start the machine on the main screen and then select Lanuch Remote Control to start the connection to the machine. If there is no remote connection add-on installed on the station to connect to the machine, download and install this package https://customerconnect.omnissa.com/en/downloads/details?downloadGroup=VMRC1205&productId=614
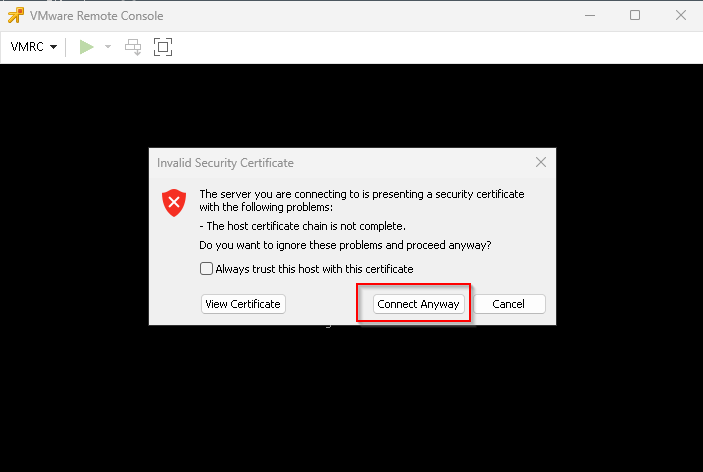
After starting the connection to the machine, you may be prompted with a certificate error, in which case select Connect anyway
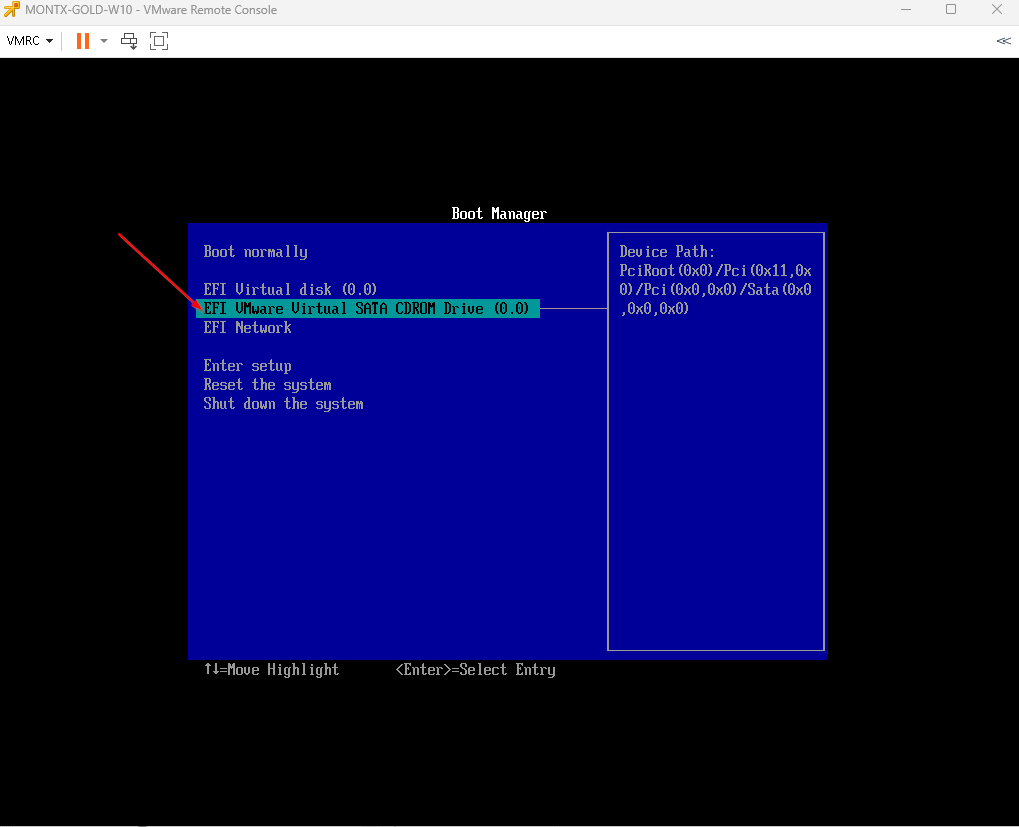
The first step is to connect the ISO to the machine go to VMRC -> Removable Devices -> CD/DVD drive 1 -> Connect to Disk Image File (iso) and then point to the ISO file with Windows 10
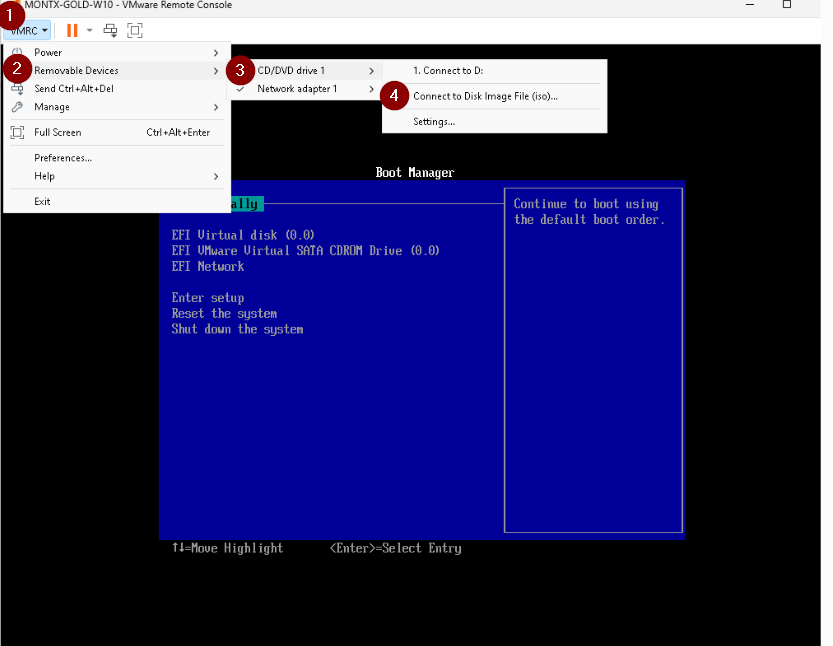
Then select the EFI Virtual SATA CDROM Drive option, the Windows installation will be launched
Next is the standard installation of Windows 10
After installation, select SHIFT CTRL F3 on the initial screen to enter audit mode, the machine will be rebooted
After startup, a window from sysprep tool will be displayed, you can close it or select Cancel
The next step is to install VMTools, to do this, go to VMRC -> Manage -> Install Vmware Tools, an ISO will be mounted to the system, run the installer by selecting the D drive and the exe file named setup64.exe
After running the installer, select Next
Typical installation type
Select install
Finally, select Finish
You will be prompted to reboot your machine, select Yes
The next step is very important, because this is the installation of Horizon agent, which communicates with the connection server, without it we will not be able to create VDI machines.
Run the agent installation file in this case it is VMware-Horizon-Agent-x86_64-2312-8.12.0-23142606.exe
Accent the license terms and conditions
Then select IPv4
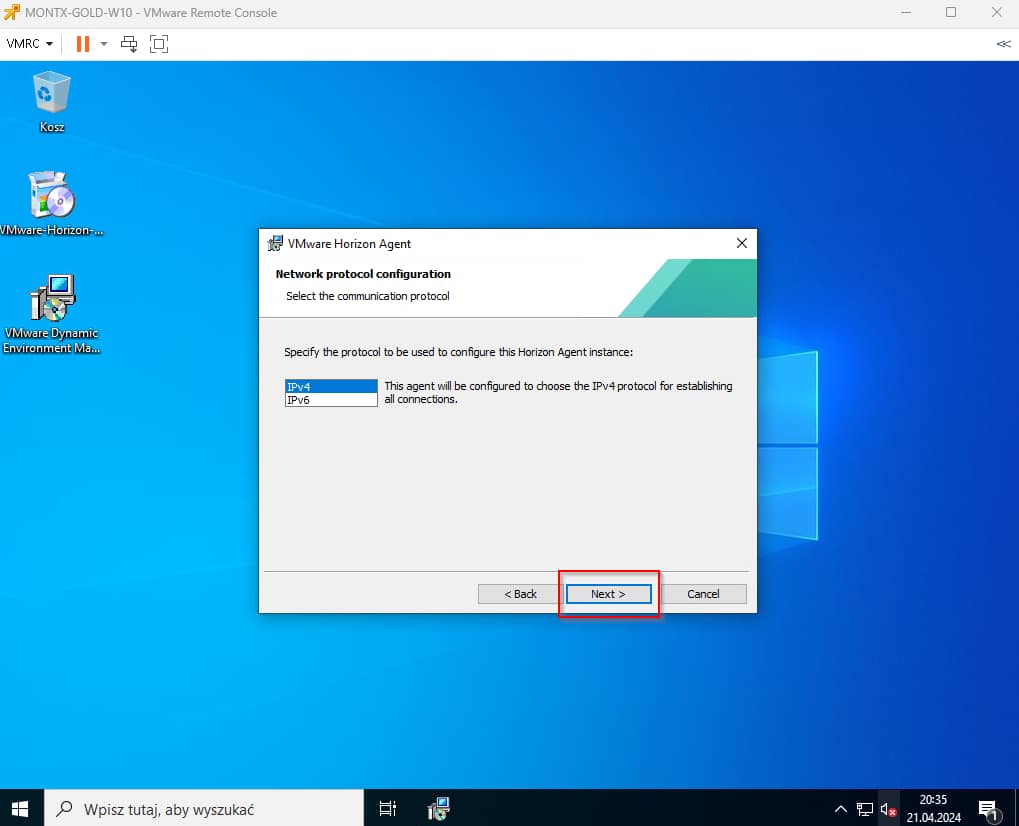
In the next stopper, select what features will be installed, below is a table with the values
| Option | Enable |
| Core | Yes |
| USB Redirection | No |
| Real-Time Audio-Video | Yes |
| VMware Horizon Instant Clone | Yes |
| Client Drive Redirection | No |
| Horizon Monitoring Service Agent | Yes |
| Scanner Redirection | No |
| Smartcard Redirection | No |
| Serial Port Redirection | No |
| VMware Audio | Yes |
| SDO Sensor Redirection | No |
| Geolocation Redirection | No |
| Horizon Performance Tracker | Yes |
| VMware Integrated Printing | No |
| Help Desk Plugin for Horizon Agent | Yes |
| Storage Drive Redirection | No |
The installer asks whether to enable RDP on the machine, select Enable
On the final screen you can indicate that after the agent installation the machine will be restarted automatically, select Install
After the reboot, install another agent which is the DEM (Dynamic Envirnoment Manger) agent, in short VMware DEM is a tool for managing end-user work environments. It allows you to capture user settings and preferences and then restore them regardless of the machine the user is working on. This allows employees to use a personalized work environment on any device, making them more productive and comfortable. On how to configure this tool from the GPO side in this article https://vdesktop.ninja/en/dynamic-environment-manager-configuration/
Run the file named VMware Dynamic Environment Manager Enterprise 2312 10.12 x64.msi on golden image
Confirm the acccetpation of the provisions of the agreement
Leave the default installation path
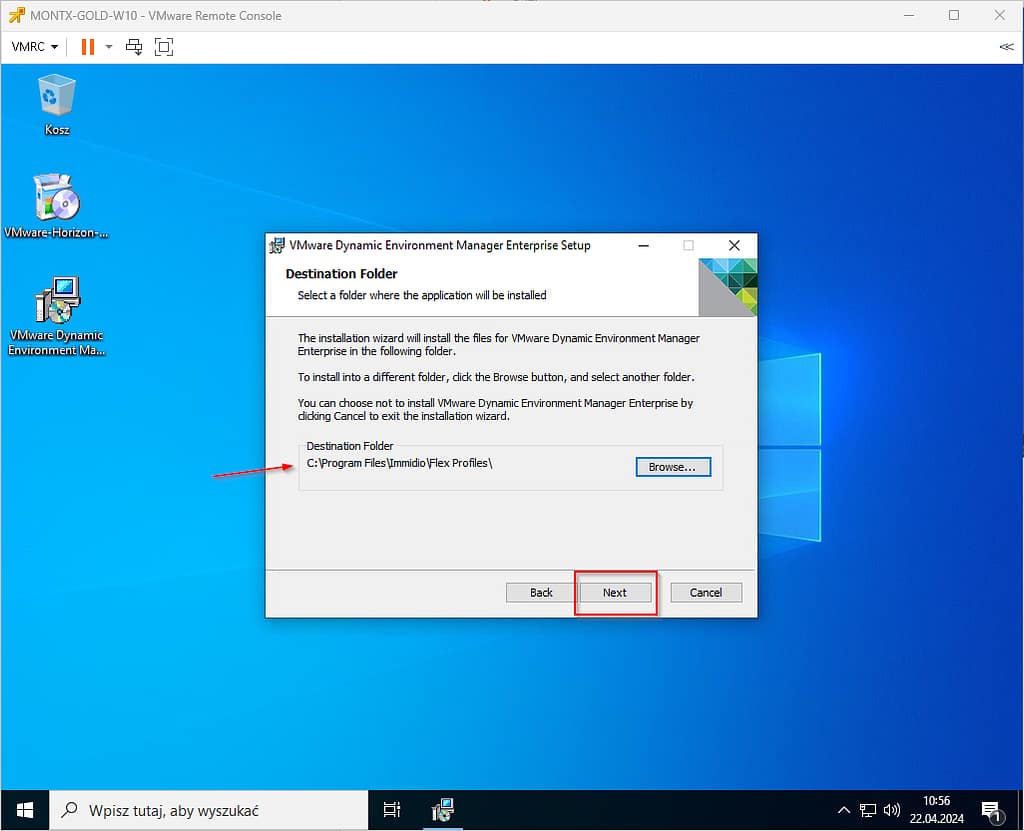
Select the Custom installation type
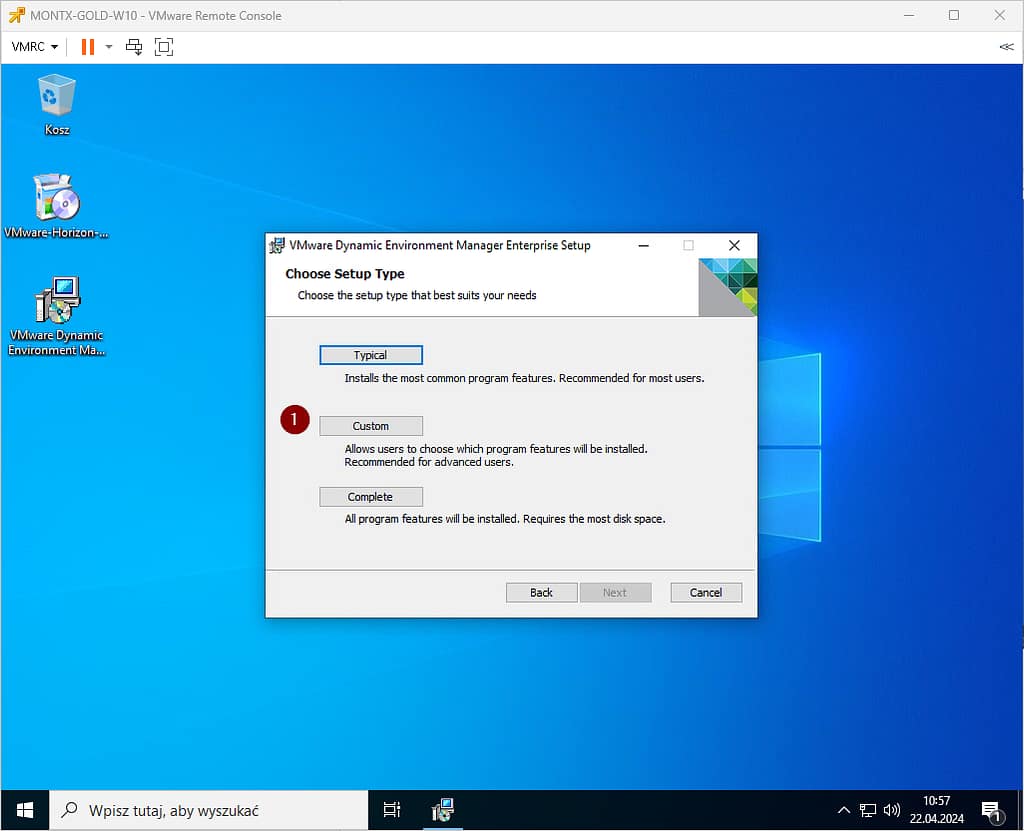
In the next step, block the installation of Application Migration and Self Support components
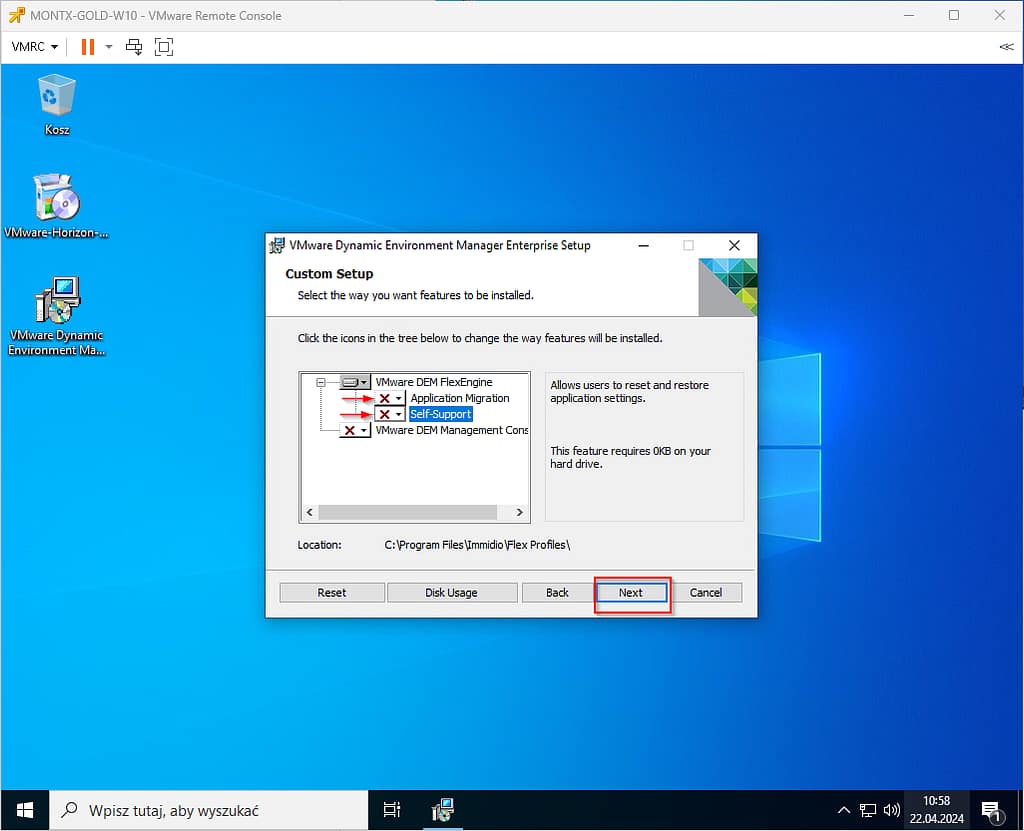
Confirm the installation of the agent
Finish the installation by selecting Finish
After installing the required agents, the next step in preparing the image is to perform a Windows update, depending on the organization this can be downloading patches directly through the Windows update service on the machine, delivery through SCCM or performing an offline installation by downloading packages from the Windows Update Catalog site.
In these cases, the patches are downloaded by the Windows Update service directly from the Internet.
The next step is to install the applications required on the user’s machine, in this case, they will be the following:
- 7zip,
- Adobe Reader,
- Chrome,
- Microsoft Office 2021 LTSC,
- MS Teams,
- Notepad ,
Installation of the application is standard nothing different from the installation on the PC, I will only note the installation of Office, because it requires the use of ODT application. It can be downloaded from here https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=49117
The next step is to generate the installation setup file, the easiest way to do this is with the wizard available at https://config.office.com/deploymentsettings
The golden image contains the setup.exe file and the O2021_PRO.xml configuration file, the first step is to run the command:
setup.exe /download O2021_PRO.xmlThis command will start downloading the files from Microsoft servers needed for the installation.
No progress is displayed during the download, once downloaded you will be able to enter the next command:
setup.exe /configure O2021_PRO.xml
The installation of Office will be started,
Upon completion, a message will be displayed that the installation is complete
After installation, delete all installation files, as they will be copied to all other machines, which will also take up disk space.
Optimize the system
After installing all the agents, patches and applications, you need to perform system optimization, you can do it manually or by using a great tool which is Windows OS Optimization Tool for VMware Horizon, you can download from here https://customerconnect.vmware.com/en/downloads/info/slug/desktop_end_user_computing/windows_os_optimization_tool_for_vmware_horizon/1_0
After downloading, run the file VMwareHorizonOSOptimizationTool-x86_64-1.2.2303.21510536.exe , the first time you run it, you must accept the terms of the license
After launching the application, select Analyze
The tool will perform an analysis and display what items can be customized, the options are many, you should verify that the selected default settings meet the expectations of our organization
For example, if there is a need to leave the appx application on the system, enter the common option
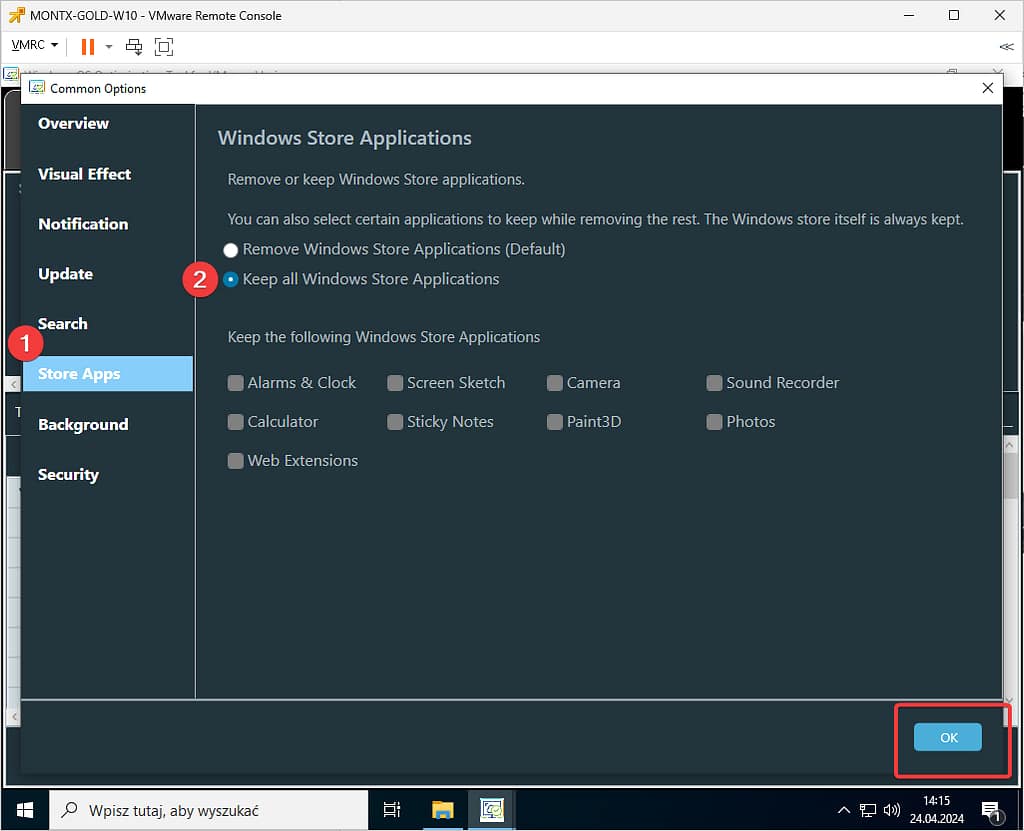
Then go to Store Apps in the left menu and select Keep all and confirm OK
After selecting the option to optimize, confirm Optimize
The optimization process will start, which will take a long while
After the optimization is done, the tool will display a report with the statuses of each item, you can save such a report using export
The next step is to perform sysprep on golden image, this tool gives you the opportunity to perform such operation. To do this, go to the Generalize tab
You can leave the default values, an important note the sysprep process deletes all data stored in the user profile named Administrator, if there are any files there that you need to keep, you should move them to a network resource. To run the process, select Generalize
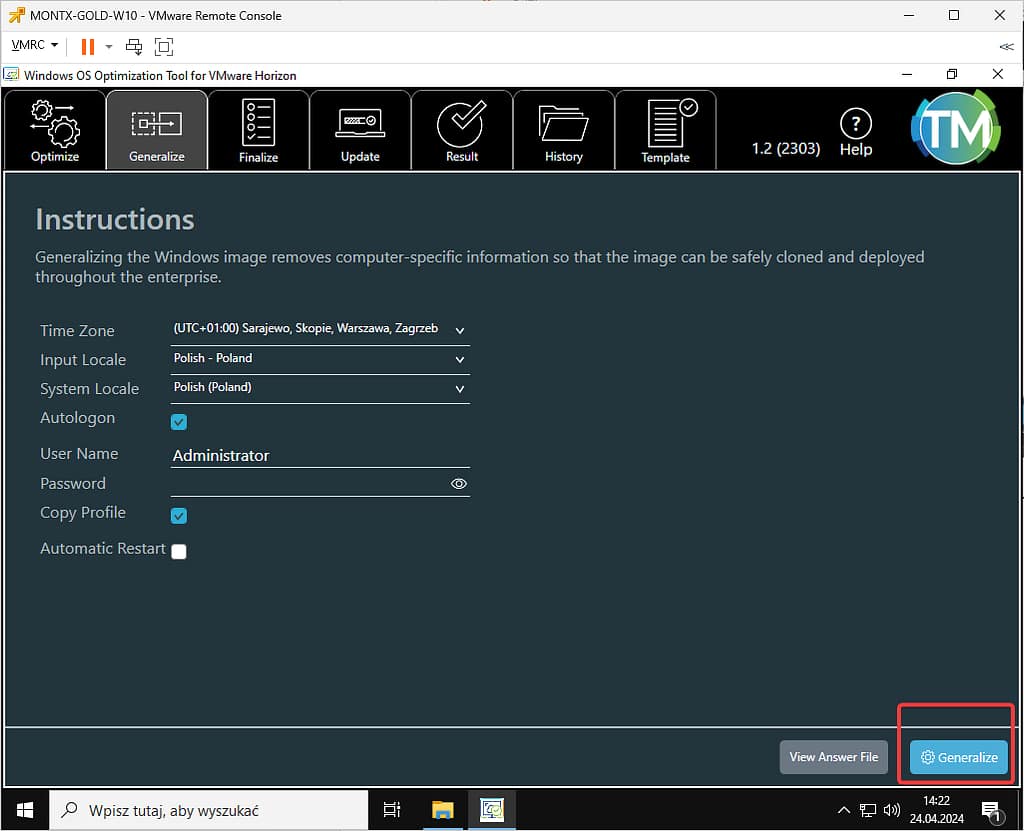
Sysprep may take a few minutes, the machine will be restarted
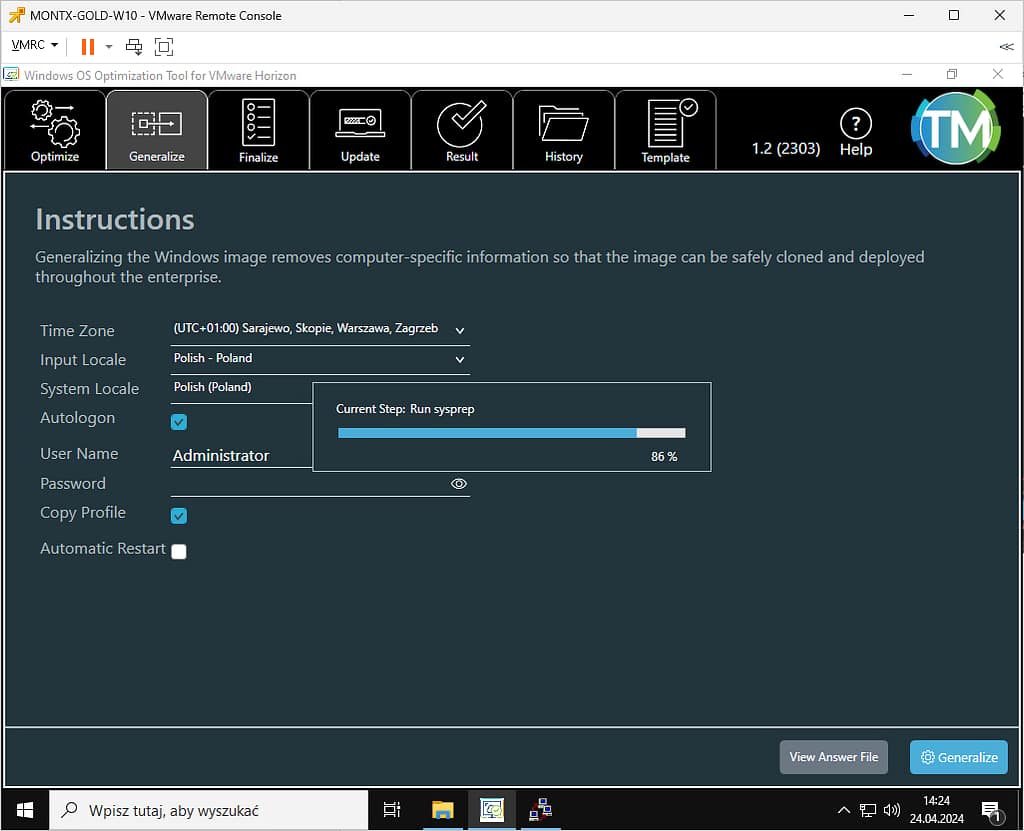
When finished, a message will be displayed
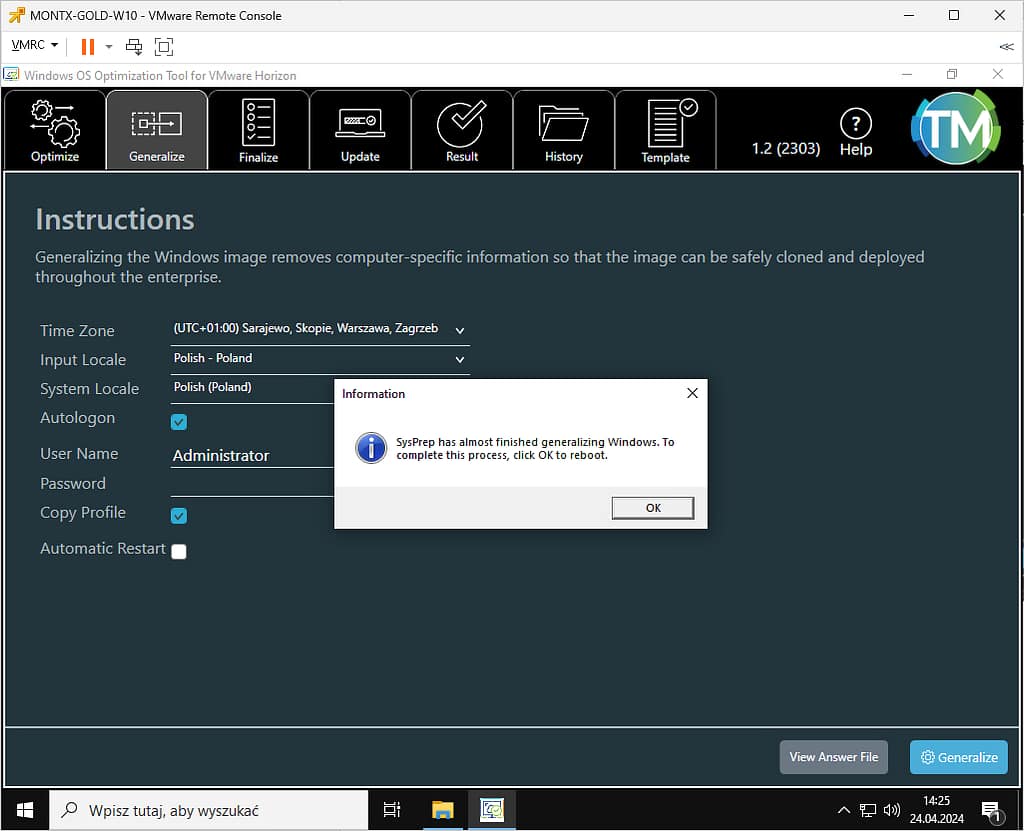
After restarting the machine, run the VMwareHorizonOSOptimizationTool-x86_64-1.2.2303.21510536.exe file, go to the Finalize tab
Leave the default settings and confirm by selecting Finalize, the process will take a few minutes
When the process is complete, you will be prompted with a message and a suggestion for the next steps, after this message, select ok, close the application and disable golden image.
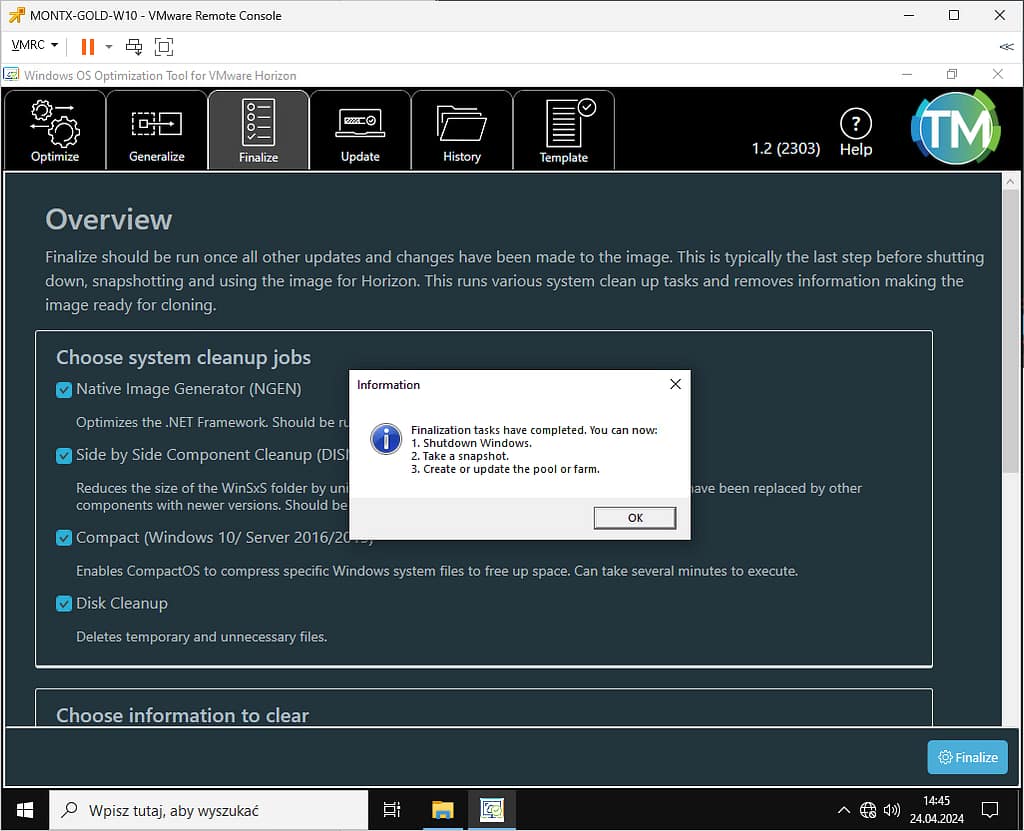
The next step is to make a snapshot, it is good practice to call the snapshot with the golden image version, such as 1.0.0 or according to the established policy in the Organization.
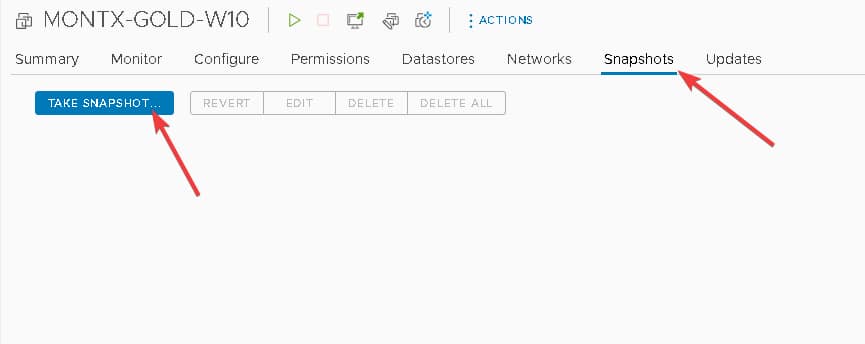
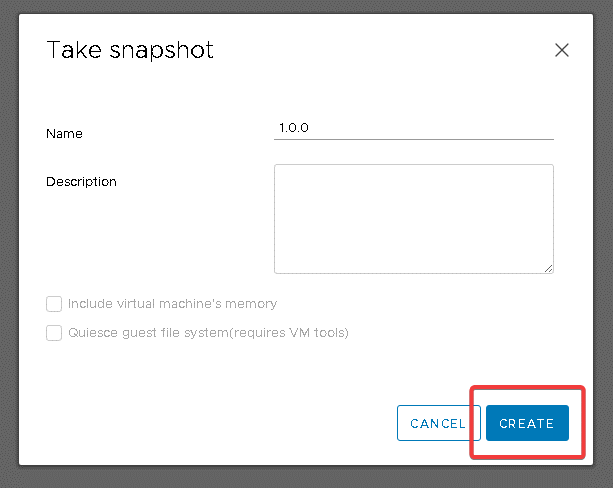
Creating a VDI pool in the Horizon panel
After going through the preparation, you need to create a VDI pool, for the best performance the instant clone technology was chosen.
Instant clone is an advanced virtualization technology that is revolutionizing the way copies of virtual machines are created. Traditionally, cloning a VM was a time-consuming process, requiring copying large amounts of data, which could take hours or even days, depending on the size of the machine and the performance of the infrastructure.
However, instant clone is changing those rules. Thanks to intelligent mechanisms and optimizations, the technology can create a fully functional, identical copy of an existing virtual machine in just seconds. Whether the virtual machine is a few gigabytes or even terabytes, instant clone handles the task in no time.
What’s more, instant clone saves valuable resources. Instead of storing full copies of each VM, which takes up a lot of disk space, instant clone uses deduplication and data block splitting techniques. This means that multiple VMs can share the same data blocks, significantly reducing storage requirements.
To create a pool, log in to the Horizon admin panel
After logging in, from the menu on the left, go to Desktops
In the Desktops panel, to add a new pool, select Add
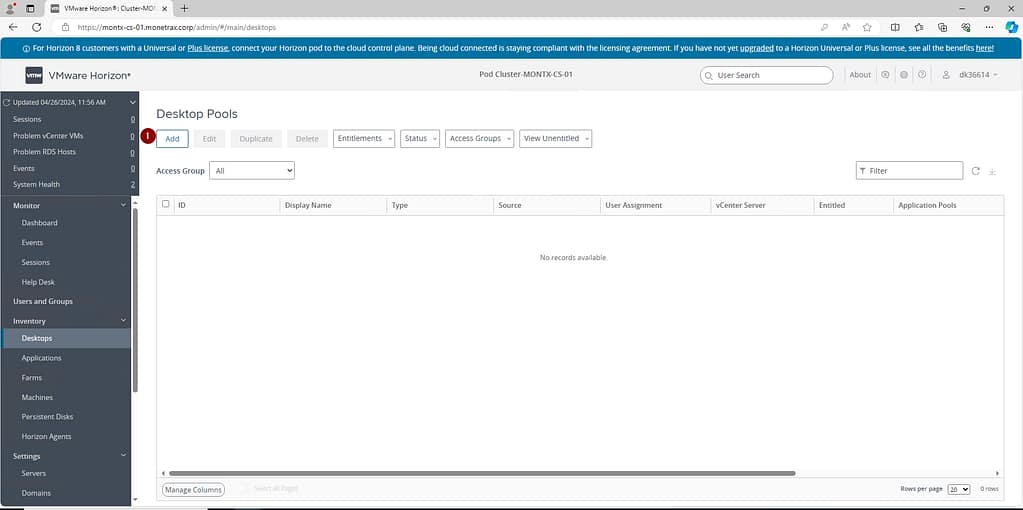
A wizard will open, in the first step you need to select the type of pool, there are three to choose from:
- Automated Desktop Pool – this option allows you to create VDI pools that are automatically hosted and managed by VMware Horizon. The number of desktops in the pool adjusts based on demand, and desktops are created based on golden image.
- Manual Desktop Pool – in this option, the administrator manually assigns desktops to the pool. This provides more direct control over the desktops, but requires more manual effort for configuration and management.
- RDS Desktop Pool – this type of pool uses Remote Desktop Services (RDS) to provide users with session-based desktops. Instead of assigning each user a dedicated virtual machine, they share an RDS host server and receive a session-based desktop. This option will work when a Farm is created in Horizon.
Monetrax will use a pool built with instant clone, so option one is selected
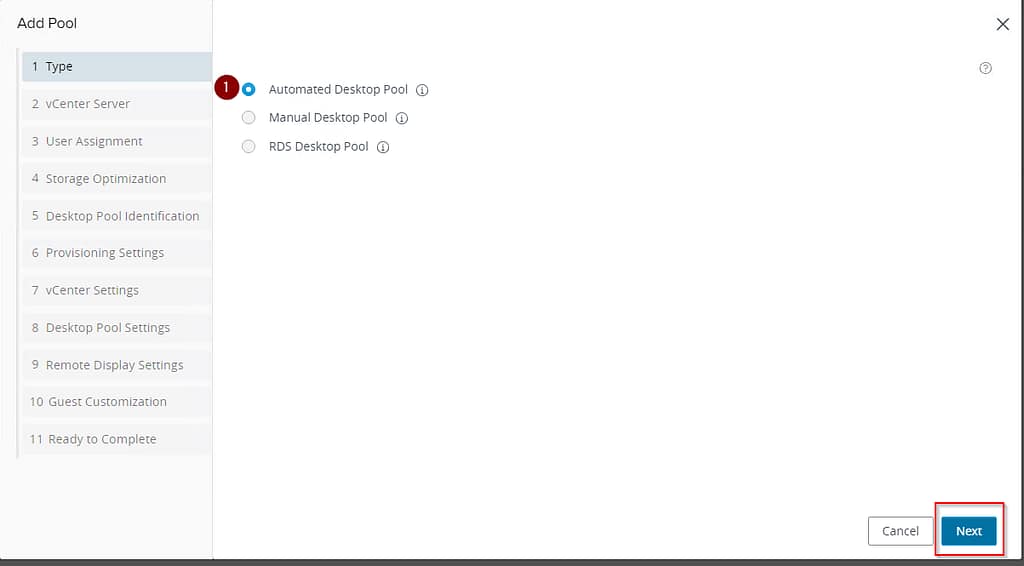
In the next step there is an option to select a vCenter if there is more than one configured, in this case there is one vCenter, in addition the Instant clone option is left. What is full clone? Full clone is a method of creating a copy of a virtual machine that creates an independent, complete replica of the original virtual machine. Unlike instant clone, full clone does not share any resources with the source machine. Instead, all data, including virtual hard disk drive (VMDK) files, configuration and settings, are copied to the new VM. The full clone process is time-consuming and requires a significant amount of disk space, as a full copy of all data is created. However, once the cloning process is complete, the new VM is completely independent of the original one. Any changes made to the full clone do not affect the source machine and vice versa.
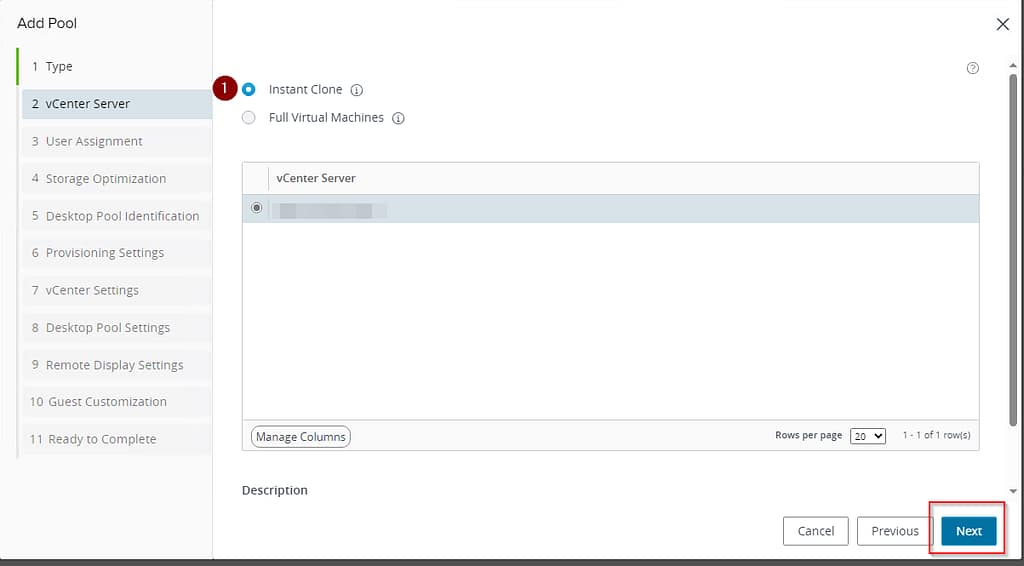
The next step allows you to choose how machines will be assigned to users.
- Floating (Variable) – in this option, VDIs in the pool are not assigned to specific users. Instead, users are given access to an available computer from the pool when they log in. After logging off, the desktop is reappointed after which it returns to the pool and becomes available to other users.
- Dedicated – in this model, each VDI in the pool is assigned to a specific user. The user always gets access to the same desktop every time he logs in. Additional options are available in this option:
- Enable Automatic Assignment – Checking this box allows VMware Horizon to automatically assign users or groups to desktops in the pool.
- Enable Multi-User Assignment: Use this checkbox to enable multi-user assignment to a pool.
The organization chose Floating, for resource and security reasons because the machine is created anew every time a user logs out.
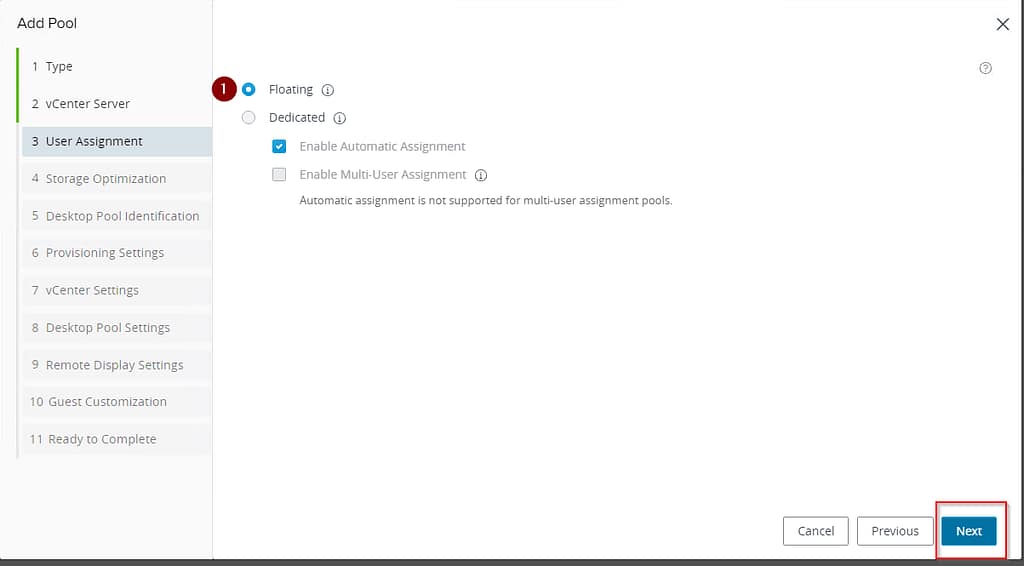
The storage selection comes in the next step, where you indicate whether the pool should use vSAN or not. This scenario assumes the use of vSAN.
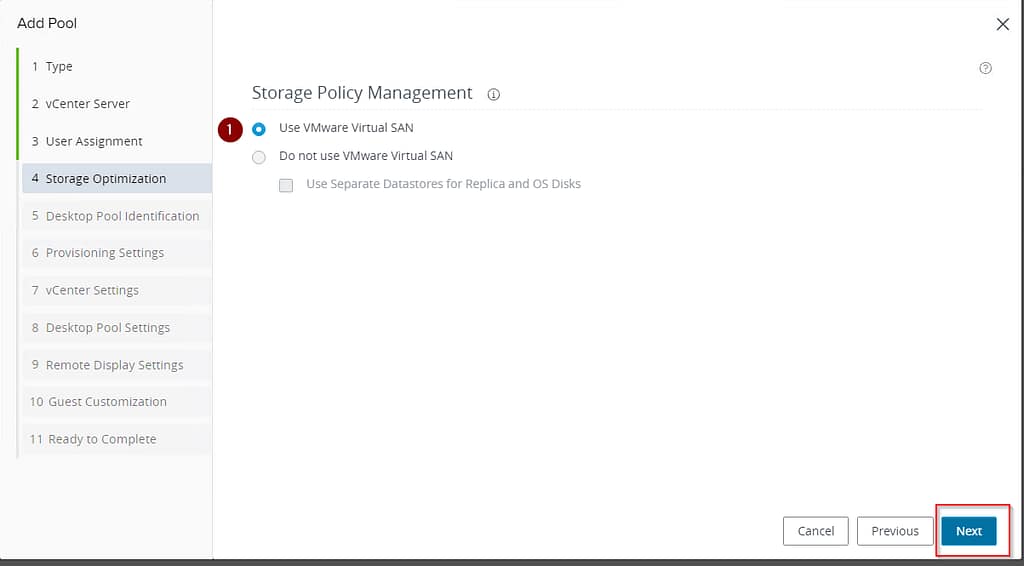
Next, you need to specify the name of the pool (ID) and what name will be presented to the users (display name), if you do not specify the display name parameter then the ID will be displayed to the users.
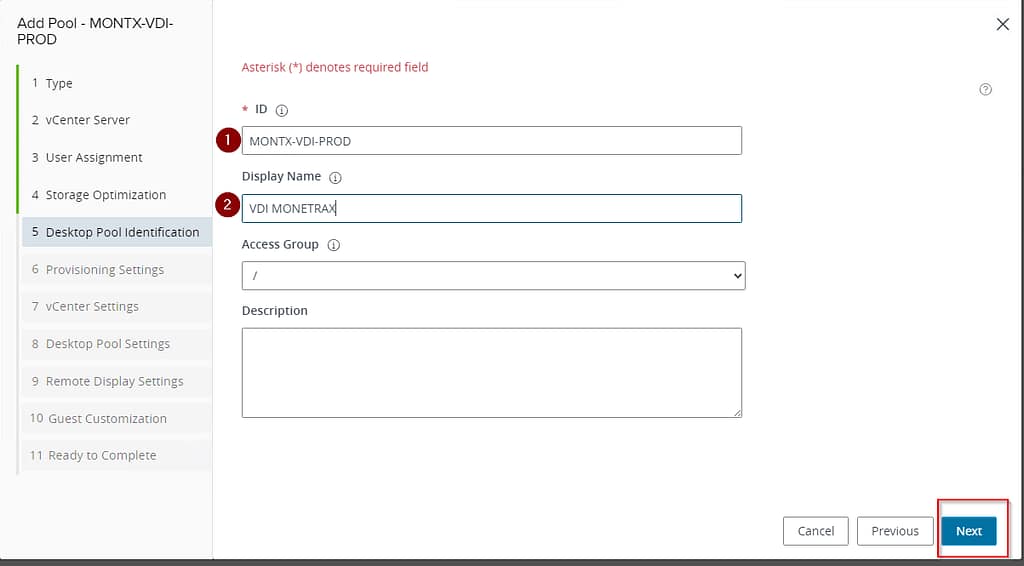
Provisioning Settings is the next stop when configuring a VDI pool in VMware Horizon. The following options are available in this step:
- Basic:
- Enable Provisioning – this option allows you to enable the provisioning process, that is, the automatic creation and configuration of virtual machines,
- Stop Provisioning on Error – checking this option stops the provisioning process in case of an error.
- Virtual Machine Naming:
- Specify Names Manually – this option allows you to manually enter names for virtual machines in the text box below,
- Use a Naming Pattern – selecting this option allows you to define a naming pattern for virtual machines in the Naming Pattern text box.
It is worth noting here how you can create a naming pattern in Horizon, the first option is to use a prefix and {n}, e.g. VDI-{n} will mean that machines will be created in the order VDI-1, VDI-2…VDI-100. The second option is to use the prefix and the expression {n:fixed=2} or {n:fixed=3}, this will mean that machines will be created with the naming VDI-01…VDI-99 or VDI-001…VDI-999.
- Provision Machines:
- Machines on Demand – in this option virtual machines are created on demand when needed. The Min Number of Machines field allows you to specify the minimum number of machines that should be available.
- All Machines Up-Front – selecting this option causes all virtual machines to be created in advance, regardless of the current demand.
- Desktop Pool Sizing:
- Maximum Machines – this field allows you to specify the maximum number of virtual machines in the pool.
- Spare (Powered On) Machines Here you can define the number of spare virtual machines that will remain powered on and ready for use.
- Virtual Device:
- Add vTPM Device to VMs – check this checkbox to add a virtual TPM (Trusted Platform Module) to VMs.
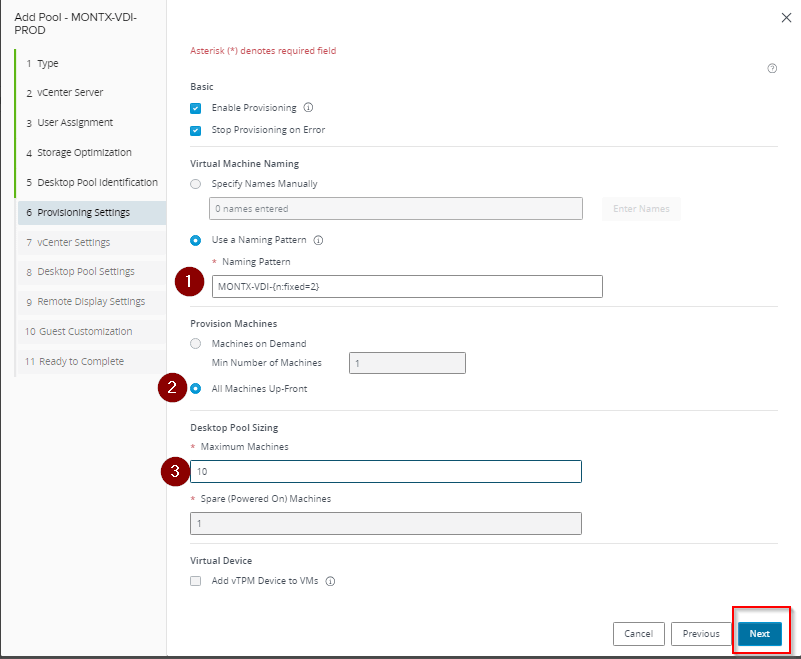
Moving on to the vCenter Settings section, you will find the following options:
- Default Image:
- Golden Image in vCenter – this field is used to specify the path to the VM’s master image file in vCenter. The Browse button allows you to browse and select the appropriate file.
- Snapshot – in this field you can select a snapshot of a virtual machine to be used as a basis for creating new machines.
- Virtual Machine Location:
- VM Folder Location – this field allows you to specify the path to the folder where the virtual machines will be stored.
- Resource Settings:
- Cluster – here you can select the cluster in which the VMs will be created.
- Resource Pool – this field is used to indicate the resource pool to which the VMs will be assigned.
- Datastores – when you click the “Browse” button, you can select the storage on which the VM files will be stored.
- Network:
- it is possible to select the network to which the virtual machines will be connected, usually Golden Image’s default network configuration selected option is left, which means selecting the same network as the one assigned to Golden Image.
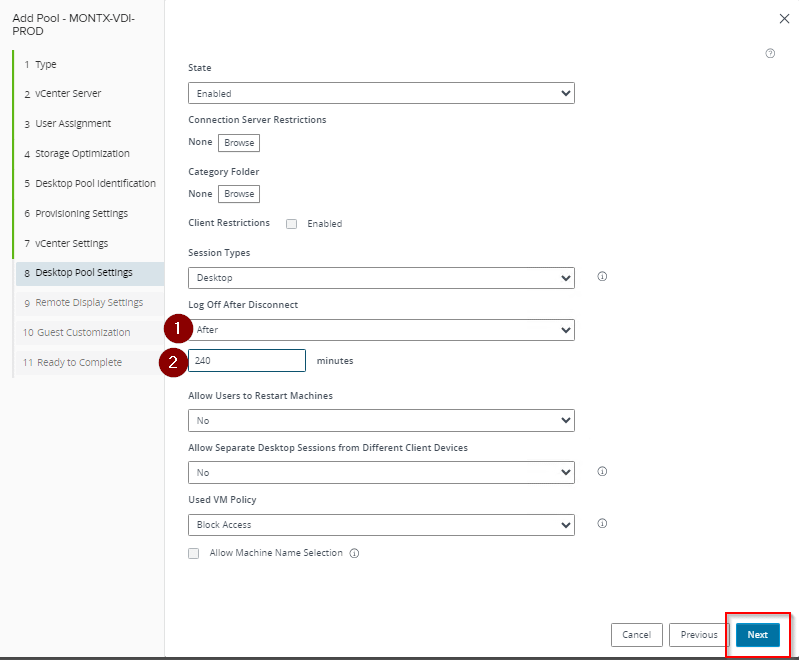
The next step is to configure the VDI pool settings, where you can find the following options:
- State – this checkbox allows you to enable or disable the desktop pool.
- Connection Server Restrictions – after clicking the Browse button, you can select the connection servers that the VDI pool will have access to.
- Category Folder – the Browse button allows you to select the category folder to which the desktop pool will be assigned.
- Client Restrictions – check this box to enable client access restrictions to the computer pool.
- Session Types – from the drop-down list you can select the type of session that will be available to pool users can be full desktop or application mode.
- Log Off After Disconnect – allows you to specify when a user will be logged off after disconnecting a session.
- Allow Users to Restart Machines – this checkbox determines whether users will be able to restart their virtual machines.
- Allow Separate Desktop Sessions from Different Client Devices – checking this option allows users to access separate desktop sessions from different devices.
- Used VM Policy – use the drop-down list to specify access policies for previously used VMs.
- Allow Machine Name Selection – checking this box allows users to choose the name of their VM.
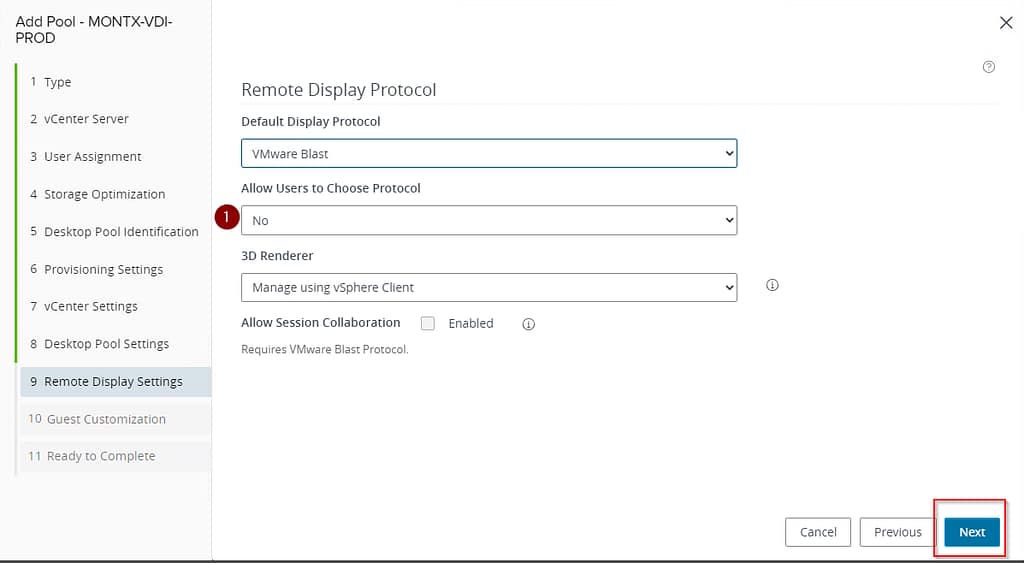
The next section deals with options for displaying the VDI pool to the end user. The options the administrator can configure are:
- Default Display Protocol – specifies which protocol will be used by default to send the remote desktop image to the client. In this case, it is VMware Blast, VMware’s optimal protocol for high performance and quality.
- Allow Users to Choose Protocol – when this option is enabled, users can choose the protocol themselves (e.g. PCoIP, RDP) when connecting to the desktop, instead of being forced to use the default.
- 3D Renderer – it is possible to choose the method of handling 3D graphics for desktops. The Manage using vSphere Client option means that 3D graphics performance settings (such as graphics card type, memory allocation) are controlled in the vSphere console for ESXi hosts running virtual desktops.
- Session Collaboration – a feature available only for the Blast protocol, allowing multiple users to connect to the same desktop at the same time and work together. Useful for technical support, training or group work. This option requires additional configuration.
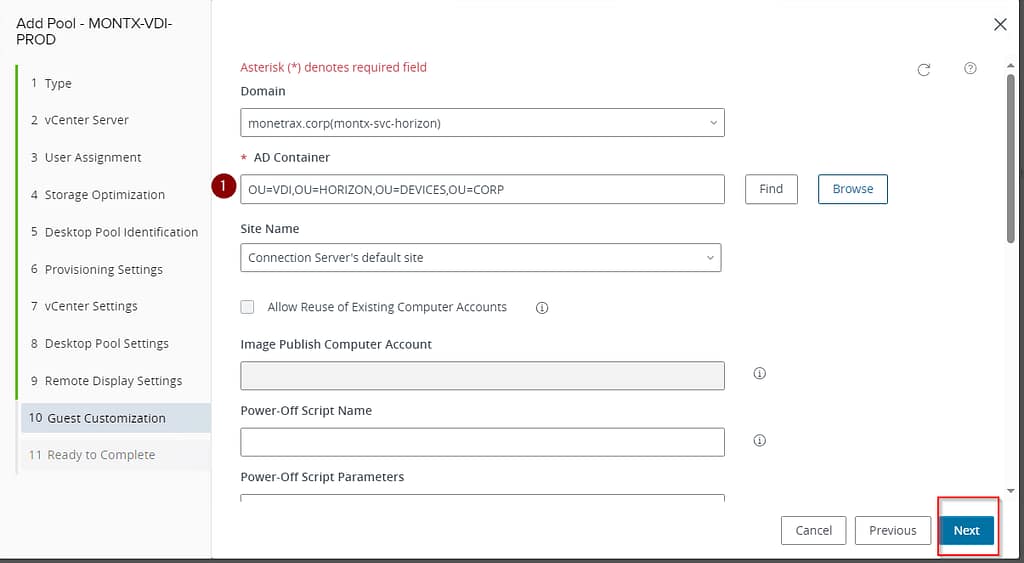
The last step is to choose the settings where in AD (in which OU) to create VDI machine accounts. The wizard allows you to configure the following options:
- Domain – the Active Directory domain where the computers are located.
- AD Container – the container in AD where the computers are located. You can search for it with the Find and Browse buttons.
- Site Name – the name of the site, by default “Connection Server’s default site”
- Allow Reuse of Existing Computer Accounts – an option that allows you to reuse existing computer accounts in AD.
- Image Publish Computer Account – image publish computer account.
- Power-Off Script Name – the name of the script executed when machines are shut down.
- Power-Off Script Parameters – parameters for the shutdown script, such as “p1 p2 p3”
- Post-Synchronization Script Name – the name of the script after synchronization.
- Post-Synchronization Script Parameters – parameters for the script after synchronization, for example, “p1 p2 p3”
- it is possible to decide whether to use ClonePrep or your own customization specification (SysPrep) to prepare systems.
What is ClonePrep?
ClonePrep is a VMware tool for customization and deployment of guest operating systems (guest OS) on virtual machines (VMs). It is an alternative to the Microsoft Sysprep tool.
Key features of ClonePrep:
- VM customization – allows you to customize settings like hostname, domain, IP address using customization specifications.
- VM Deployment – enables mass deployment of personalized VMs based on templates or existing machines.
- Manage network settings – configure IP addresses, DNS, WINS, guest domains.
- Run scripts – can execute scripts during and after system customization.
ClonePrep is part of VMware vCenter and works with Windows and Linux systems. It simplifies and automates the process of preparing multiple identical VMs with personalized settings. In the context of VMware Horizon, ClonePrep is often used for bulk provisioning of VDI desktops with user-specific customization. It allows administrators to easily deploy large numbers of desktops with appropriate settings, which is crucial in VDI environments.
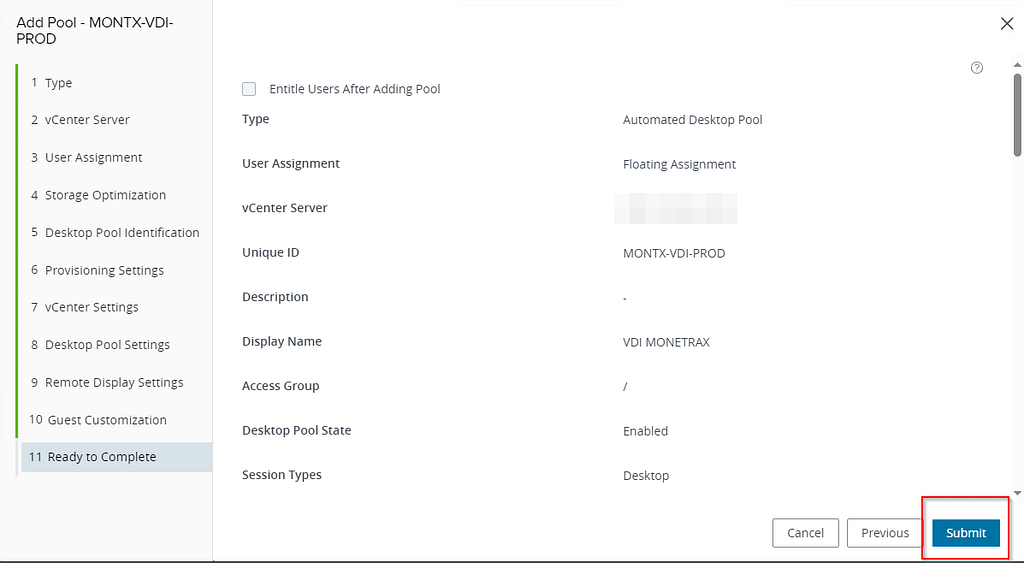
Finally, a summary of the settings selected earlier is displayed. The Submmit button will start the VDI creation process.
The progress of pool creation can be tracked by entering the properties of the pool, by clicking on its name.
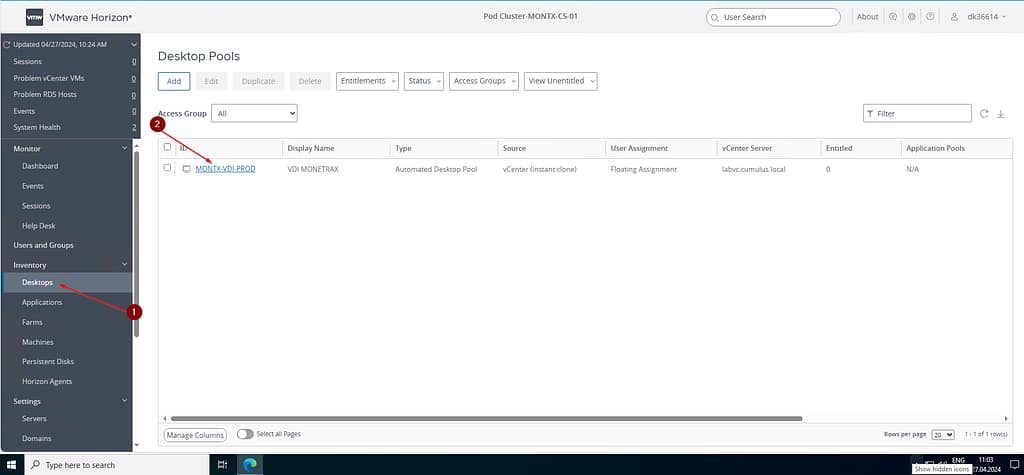
In the pool properties, after scrolling down, you can see a progress bar.
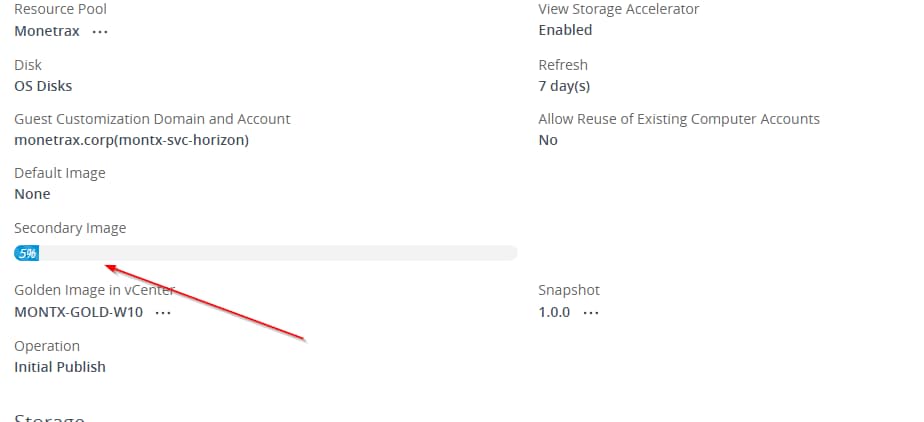
Once the machine creation is complete, you need to add permissions for users to be able to log into VDI machines. If permissions are not added the administrator console in the pool will display a message.
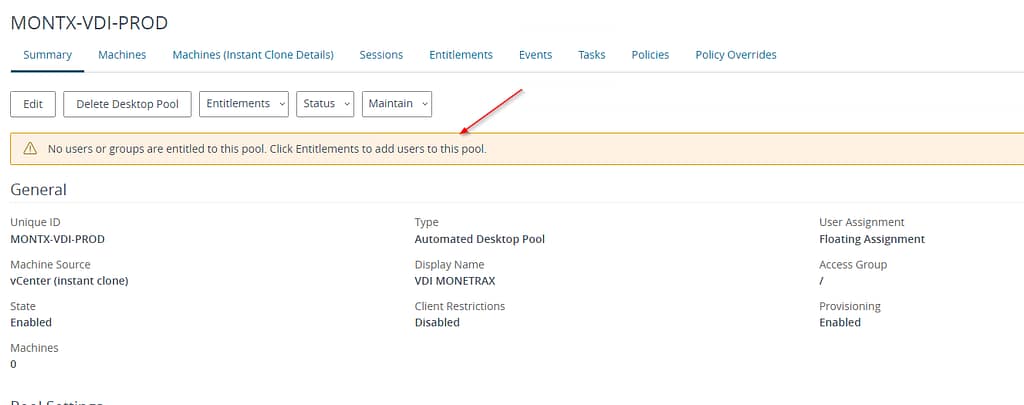
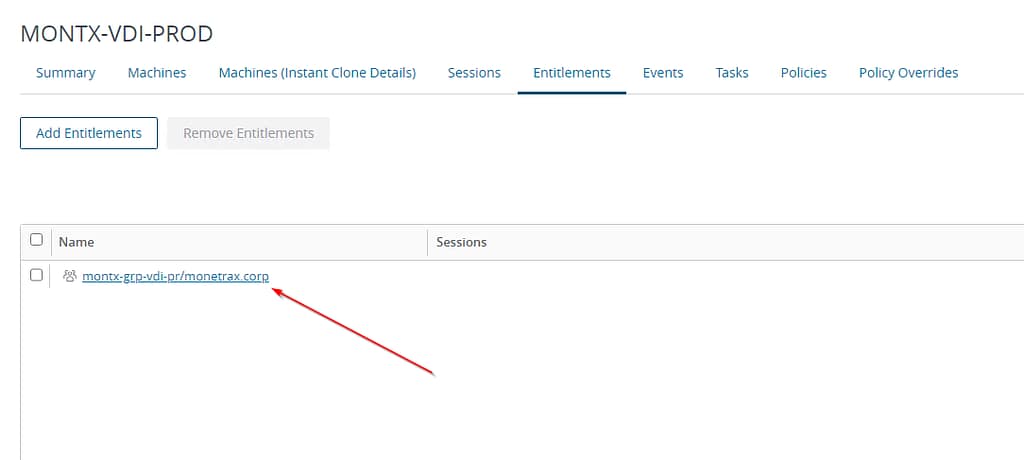
To add permissions, go to the Entitlements tab and then select Add Entitlements
In the window that opens, you can search for individual users or groups. You need to enter a name, select Find and select the object of your choice.
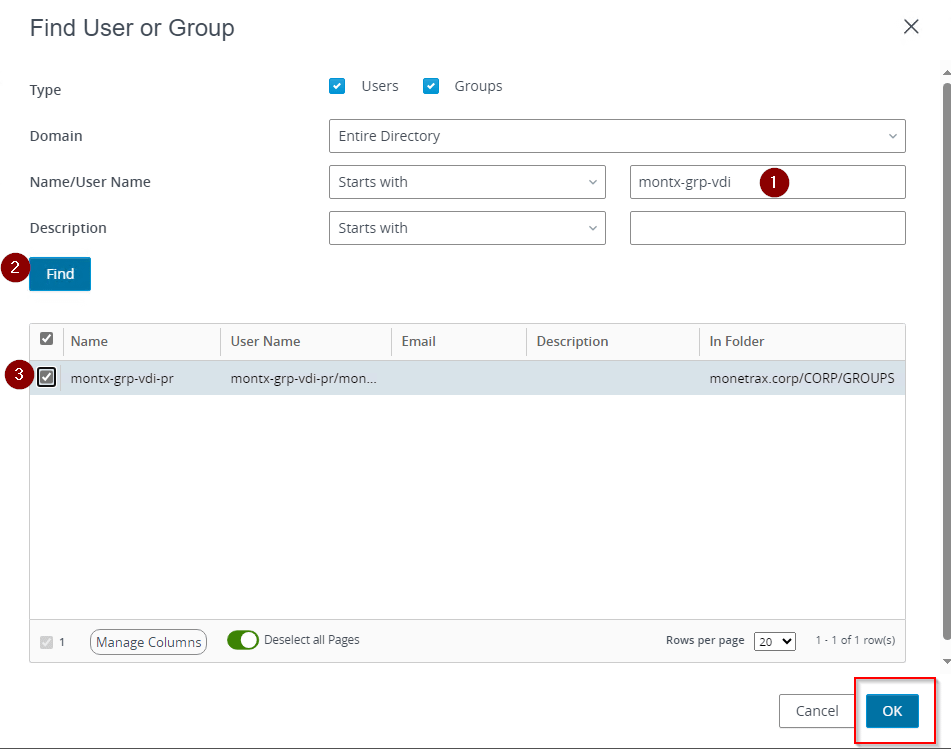
After adding a group, the Entitlements tab will show an entry